sweet, ageing poison | by juliette scarfe
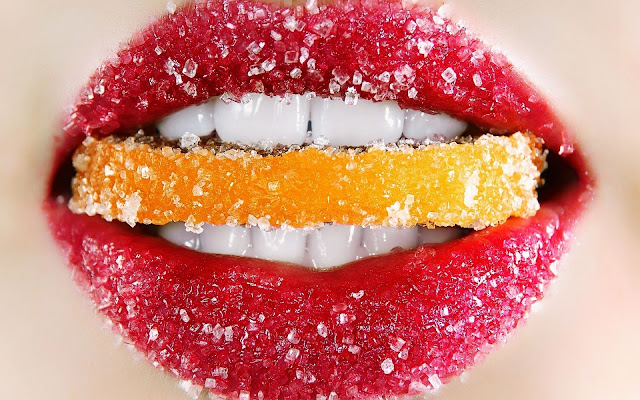 |
| Image source > |
(A guest post by Juliette Scarfe of BareSkin Beauty)
Sugar has become our constant companion in modern society. Whether added to our hot drinks, or hidden in our favourite packaged and processed foods, it’s hard to imagine life without sugar. With obesity and degenerative disease levels increasing exponentially its important to understand just how sugar can wreak havoc on your health and wellbeing. Here we discuss the truth about sugar and natural alternatives available on the market.
Every living creature is designed to run off of a simple sugar called glucose. It is the primary unit in the study of metabolism. However, there are dangers involved with consuming excessive amounts of glucose, including: elevated blood sugar and insulin, which trigger fat accumulation, cellular inflammation and insulin resistance.
“The average Brit consumes a shocking 1.25lbs of sugar a week”
“The average American consumes in excess of 22 teaspoons a day”
“In 2009, the average individual consumes 150 pounds of sugar per year. Half of our society consumes ½ pound of sugar per day”
THE BIOCHEMISTRY OF SUGAR
Sugars are carbohydrates and are composed of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. Simple sugars are called monosaccarides and include glucose (also known as dextrose), fructose and galactose. Table/granulated sugar is sucrose (half fructose, half glucose), a disaccaride. Other disaccharides include maltose and lactose.
The chemistry of sugar is based on the number of carbohydrates and includes monosaccharides, disaccharides and oligosaccharides. The most important monosaccarides are glucose, dextrose, and fructose. The primary difference in these carbohydrates is the way they are digested and metabolized. Glucose and dextrose are basically the same form of sugar.
“Sugar can be intoxicating, it is processed by the liver as alcohol”
FRUCTOSE AND ITS EFFECT ON THE BODY
Fructose is another simple sugar that is found in nature within fruits, honey, and plant/tree nectar. This is metabolized differently than glucose and can also cause hazardous effects, when consumed in excess.
THE MAIN METABOLLIC DIFFERENCES BETWEEN FRUCTOSE AND GLUCOSE
- After eating fructose, most of the metabolic burden rests on your liver. But with glucose, your liver has to break down only 20%.
- Every cell in your body, including your brain, needs glucose and “burns it up” immediately after ingestion. By contrast, fructose is primarily converted into free fatty acids (FFAs), VLDL (the damaging form of cholesterol), and triglycerides, which get laid down and stored as fat.
- The free fatty acids created during fructose metabolism accumulate as fat droplets in your liver and skeletal muscle tissues, causing insulin resistance and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Insulin resistance is now extremely common and will lead to metabolic syndrome and type II diabetes.
- Fructose is the most lipophilic carbohydrate, converting to activated glycerol (g-3-p), which turns free fatty acids into triglycerides. The more g-3-p you have, the more fat you will store. Glucose does not have this same effect on the body.
- When you eat 120 calories of glucose, less than one calorie is converted to, and stored by the body as fat. In contrast, 120 calories of fructose consumed, results in 40 calories being stored as fat.
- The metabolism of fructose by your liver numerous waste products and toxins, including high levels of uric acid, which triggers the body to store fat, causing you to gain additional weight. Glucose does not produce toxins in the liver.
- Glucose suppresses the hunger hormone ghrelin and stimulates leptin, which effectively suppresses your appetite. Fructose has no effect on ghrelin and interferes with your brain's ability to communicate with leptin, resulting in scientifically proven overeating.
THE HISTORY OF SUGAR CONSUMPTION
Historically, around 1000 years ago, sugar was used in a variety of ways, such as:
- For medicinal purposes
- As a preservative
- As a spice
- As a sweetener
SUGAR PRODUCTION AND THE ENVIRONMENT
Sadly, the environment is negatively affected by sugar production all over the world. Sugar cane is a highly water intensive crop, grown under monoculture conditions, which depletes trace minerals in the soil and leads to soil erosion. Refined sugar is responsible for the greatest loss of biodiversity than any other crop. Forests and natural habitats are destroyed and cleared to make way for sugar crops and excessive amounts of fossil fuel are needed in the production process.
Therefore reducing your intake of sugar is not just beneficial for your health, but also for the planet. Consumers drive demand and therefore the environmental destruction that is inherent with sugar production.
THE BIOCHEMISTRY OF SUGAR
Most forms of sugar (except fructose) metabolize quickly in the body into a simple glucose form. This glucose is then funneled into cells by the hormone insulin to provide us with energy. This process is performed very well in our bodies, when the cells are kept sensitive to the circulating insulin.
Modern lifestyle behaviors of excessive sugar intake, processed foods and lack of movement lead to chronically elevated blood sugar and insulin levels. Creating a cellular resistance to insulin, excessive free radical damage and inflammation throughout the body.
ELEVATED LEVELS OF SUGAR AND INSULIN MANIFESTS AS:
- Mal-coordinated immune system and reduction in functional ability.
- Excess sugar in the bloodstream is very damaging, in a process called glycosylation sugar (glucose) in the blood attaches itself to proteins until they can no longer function properly. All the cells in our bodies are partly made of proteins, if the protein becomes coated with glucose, the cell cannot get to its destination or do its job, repair or regenerate.
- Dehydrated cells (particularly skin cells) and depleted levels of critical electrolytes such as: potassium, magnesium, calcium, and sodium leading to cell death (apoptosis) and chronic muscle pain and spasms.
- Depleted levels of trace minerals chromium, copper, and zinc and other trace minerals that help sensitize cells to insulin. This further accelerates cell membrane insulin resistance
- Increased cancer cell division and proliferation and inhibited cellular mechanisms that slow down tumor growth and inhibit cancer cell apoptosis (programed cell death)
- Creates tissue damaging Advanced Glycolytic Enzymes (AGE’s)
- Depletes the body of vital anti-oxidants such as glutathione, vitamin C & vitamin E.
- Inhibits Human Growth Hormone (HGH) and elevates cortisol levels (the fight of flight hormone) which causes excessive stress on the digestive system
- Inhibits cellular protein synthesis, which results in dysfunctional bone, muscle, and joint chemistry. This accelerates the risk of osteoporosis, osteoarthritis, and chronic muscle and joint pain.
- Promotes the growth of pathogenic bacteria and parasites such as Candida and other yeast like organisms. This also depletes the body of good bacteria and can lead to chronic infections in the gut, respiratory tissue and sinuses.
- Leads to obesity, elevated triglycerides, abnormal LDL:HDL cholesterol levels, elevated arterial inflammatory risk factors.
- Opens up the blood brain barrier, depletes the brain of trace mineral stores and allows toxins and other heavy metals to accumulate in brain tissue leading to cellular death and inflammation.
- Destroys nerves leading to chronic pain, neuropathies, vision disorders, and accelerated organ dysfunction.
In humans, sweet receptors evolved in ancestral environments poor in sugars and are thus not adapted to high concentrations of sweet compounds. Research indicates that sugar consumption generates a supranormal reward signal in the brain, with the potential to override self-control mechanisms and thus to lead to addiction, obesity and degenerative disease.
There are more than 70 health disorders that are connected to sugar consumption. Some of the most common are: diabetes, poor brain development in children, lack of concentration, allergies, asthma, ADHD, hypoglycemia, mood swings, immune and nutritional deficiencies.
“In the US, Dr Robert Lustig (“Sugar: The Bitter Truth”) has called for a tax on sugar similar to those placed on alcohol and tobacco due to its toxic nature”.
High sugar intake increases advanced glycation end products (AGEs) and generates free radicals and oxidative stress. Advanced glycation end products (AGEs) are a complex group of compounds formed when sugar reacts with amino acids, either in the food you eat or within the body.
There is mounting scientific evidence that AGEs may be implicated in the development of the chronic degenerative diseases associated with advanced aging, including: Cardiovascular disease, Alzheimer's disease, and Diabetes.
Of all the sugars, fructose in particular is an extremely potent pro-inflammatory agent that creates AGEs and speeds up the aging process. It also promotes the kind of dangerous growth of fat cells around your vital organs, and in particular around your waistline, that are the hallmark of high cholesterol, diabetes and heart disease.
To reduce the levels of AGEs in your body and the consequent stress your immune system experiences in order to defend against them, reduce your total fructose consumption below 25 grams per day.
For those of us that suffer from acne, excluding sugar is extremely beneficial for your skin. People who have acne do not process sugar. Insulin is the hormone that shifts sugar (glucose) out of the bloodstream and into the cells, where we use it for energy. People with acne do not transfer sugar into their cells properly.
Collagen forms an integral part of the skin’s structure, if it is damaged by oxidation (think of biting into an apple and leaving it, the apple skin oxidises and becomes brown almost immediately). Oxidation causes our skin to become saggy and wrinkled. Also affected is the efficiency with which the skin cells are nourished, supplied with oxygen and eliminate waste, leading to dull, tired and congested skin.
This is not limited to sugar, but also to refined carbohydrates such as white flour and breakfast cereals, which are converted into glucose during digestion. If we do not use these sugars for energy, immediately, they are laid down as fat cells, these fats decrease the oxygen supply to cells, particularly those in the skin – leading to dull, congested and saggy skin that repairs and regenerates at a much slower rate.
Sugar interferes with the way that the body uses vitamin C, which is needed for the formation of collagen and elastin and to support our overall health and immunity.
“Sugar causes a loss of tissue elasticity and function, the more sugar you eat the more elasticity and function you lose, leading to premature ageing.”
HOW TO TAME YOUR SUGAR CRAVINGS - Refined Sugar Alternatives:
This will be the subject of the next upcoming article here on BetterRaw.com. If you'd like to see and sample a variety of sugar alternatives, as well as incredible raw food dessert recipes, which can be produced with healthy sugars, check out Tanya Alekseeva's class Raw Food Sweet Sensations>>
For more from Juliette Scarfe, the natural health guru, natural aesthetician and founder of organic skincare range, Bareskin Beauty, visit www.bareskin-beauty.co.uk and connect with her on Twitter @baresknbeauty.
For more from Juliette Scarfe, the natural health guru, natural aesthetician and founder of organic skincare range, Bareskin Beauty, visit www.bareskin-beauty.co.uk and connect with her on Twitter @baresknbeauty.